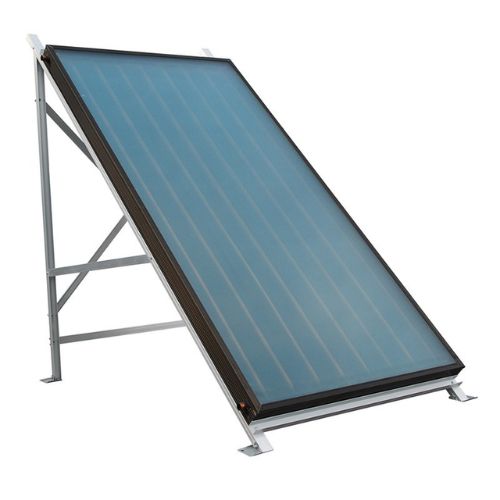
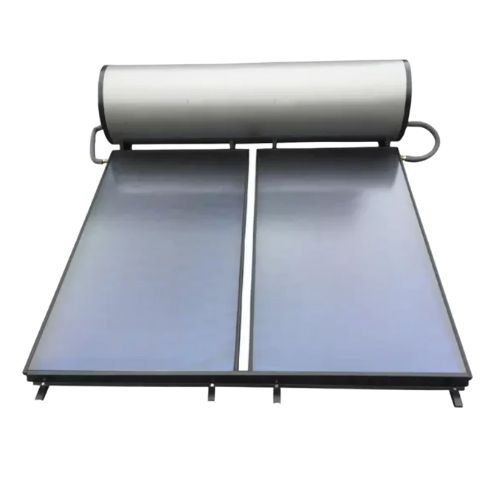
Complete guide of Solar Collector
A Solar Collector is a key component in solar energy systems, designed to absorb sunlight and convert it into heat. Solar collectors are the heart of solar thermal systems, whether used for water heating, space heating, or other applications. These devices play a crucial role in harnessing solar energy and are used in a variety of settings, from residential homes to large industrial installations. Solar collectors are efficient, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective solutions for reducing dependence on traditional energy sources and lowering energy costs.
Solar collectors come in different types, including flat plate collectors, evacuated tube collectors, and concentrating collectors. Each type is suited for specific climates and energy needs. The choice of solar collector depends on factors such as location, budget, and the desired performance.
What is a Solar Collector?
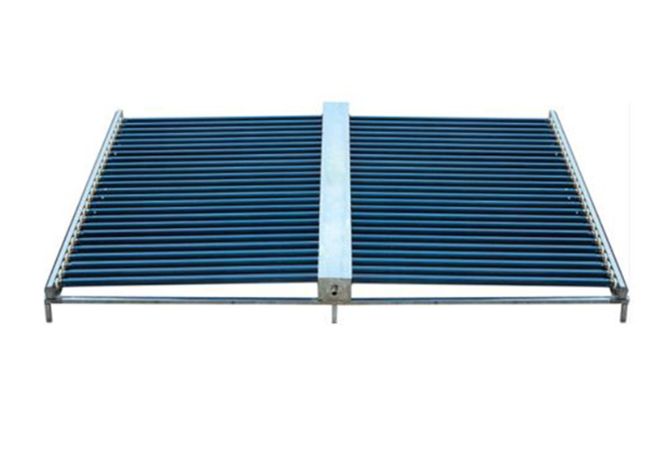

A Solar Collector is a device that captures solar radiation and converts it into usable heat. It is an essential component in solar water heating systems, solar air heating systems, and solar-powered space heating. Solar collectors can be broadly classified into two categories: passive and active systems. In active systems, pumps or fans are used to circulate heat-absorbed fluids, whereas passive systems rely on natural circulation.
Solar collectors work by absorbing sunlight through a solar absorber material, typically a blackened surface, which increases its efficiency in heat absorption. The heat is then transferred to a fluid—often water or antifreeze—which is circulated through pipes or tubes. This heated fluid can be used for various applications, such as hot water supply or space heating.
Components of a Solar Collector
-
Absorber Plate The absorber plate is the surface that directly absorbs sunlight. Typically, it is made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum, and is often coated with a selective surface that maximizes heat absorption while minimizing heat loss. The blackened surface of the plate helps absorb more solar energy.
-
Glass Cover The glass cover is used to trap sunlight and reduce heat loss. It is often made of tempered glass or acrylic, designed to allow maximum sunlight transmission while providing insulation. The cover also protects the absorber plate and helps maintain the efficiency of the solar collector.
-
Heat Transfer Fluid The heat transfer fluid is the medium that absorbs the heat from the absorber plate and carries it to the storage tank or heating system. In solar thermal systems, water or a water-glycol mixture is commonly used as the heat transfer fluid. This fluid circulates through pipes or tubes in the collector, where it is heated by the sun.
-
Insulation Insulation is essential to minimize heat loss from the collector. It is typically applied to the back and sides of the solar collector. Insulation materials, such as fiberglass, foam, or rock wool, help keep the heat within the collector and prevent energy loss.
-
Frame The frame provides structural support to the collector and ensures that all the components are held in place. The frame is often made from durable materials, such as aluminum or galvanized steel, to resist corrosion and enhance longevity.
Types of Solar Collectors

-
Flat Plate Solar Collectors Flat plate solar collectors are the most common type of solar collector, especially for residential applications. They consist of a flat, horizontal panel that is mounted on the roof or other locations with optimal sun exposure. These collectors are relatively simple and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for homeowners.
-
Evacuated Tube Solar Collectors Evacuated tube collectors are a more advanced option, often used in colder climates or for applications requiring higher temperatures. They consist of a series of glass tubes with a vacuum between the inner and outer layers, which helps reduce heat loss and improve efficiency. These collectors are more expensive than flat plate collectors but provide better performance in colder weather.
-
Concentrating Solar Collectors Concentrating solar collectors use mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a small, highly efficient absorber. These collectors are typically used for industrial applications or large-scale solar thermal systems. Concentrating collectors can achieve very high temperatures, making them ideal for power generation or processes requiring high heat.
Advantages of Solar Collectors
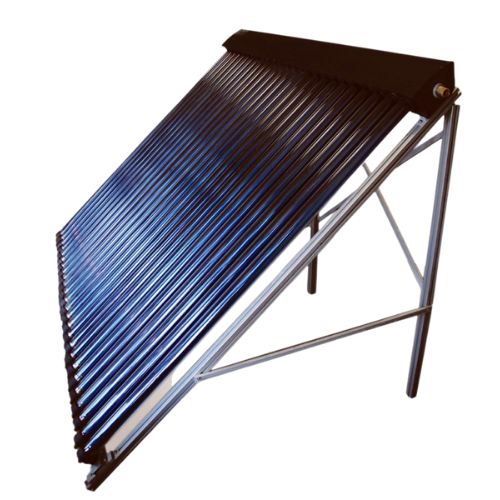

-
Energy Efficiency Solar collectors harness the sun’s energy, providing a sustainable and renewable source of heat. These collectors are highly efficient in converting sunlight into usable thermal energy, helping reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower energy bills.
-
Environmentally Friendly By using solar energy, solar collectors contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. They provide an eco-friendly solution to energy needs, reducing the overall carbon footprint of households and businesses.
-
Cost-Effective While the initial installation cost of solar collectors can be higher than traditional energy systems, the long-term savings on energy bills make them a cost-effective solution. Solar energy is free, and with proper maintenance, solar collectors can last for many years, providing consistent performance.
-
Low Maintenance Solar collectors require minimal maintenance, especially flat plate collectors. Routine checks to ensure there are no blockages or leaks and occasional cleaning of the glass surface are usually sufficient to maintain optimal performance.
-
Versatile Applications Solar collectors can be used in various applications, including heating water for residential homes, space heating, and even powering large-scale industrial processes. The versatility of solar collectors makes them suitable for diverse needs, from small households to large businesses.
Common Problems with Solar Collectors
-
Weather Dependency Solar collectors depend on sunlight to function, which means their performance can be affected by weather conditions. On cloudy or rainy days, the efficiency of solar collectors may be lower. However, incorporating backup systems, such as electric heaters, can help ensure a continuous supply of hot water or heat.
-
Space Requirements Solar collectors require adequate space for installation, especially flat plate and evacuated tube collectors. This can be a limitation for buildings with limited roof space or for installations in areas with less sunlight exposure.
-
Initial Cost The initial cost of solar collectors, especially evacuated tube and concentrating collectors, can be higher compared to traditional heating systems. However, the long-term energy savings make these systems a worthwhile investment over time.
-
Performance Fluctuations The performance of solar collectors can vary depending on the time of day, season, and geographic location. In regions with limited sunlight or during winter months, solar collectors may not perform as efficiently, requiring additional energy sources to meet heating needs.
Factors to Consider When Buying Solar Collectors
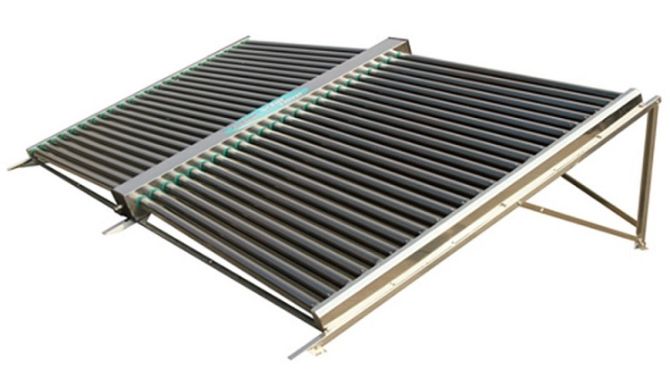
-
Collector Type Choose the type of solar collector that best suits your needs and climate. Flat plate collectors are suitable for moderate climates, while evacuated tube collectors are better for colder regions. Concentrating collectors are ideal for industrial applications requiring high heat.
-
Size of the System The size of the solar collector system should match your energy requirements. Larger systems are needed for households with high hot water demands or businesses with extensive heating needs. Ensure that the collector size and tank capacity are appropriate for your specific needs.
-
Efficiency Rating Look for solar collectors with high efficiency ratings, as these systems will provide more heat per unit of sunlight absorbed. Efficiency can vary between different types of collectors, so choosing the right system for your location and needs is important.
-
Durability Solar collectors should be durable and able to withstand environmental conditions. Look for collectors made from high-quality materials that are resistant to corrosion, UV degradation, and other weathering factors.
-
Warranty and Support Check the warranty provided by the manufacturer. A good warranty ensures peace of mind and covers any potential issues or repairs during the system’s lifespan. Also, ensure that customer support is readily available in case assistance is needed.
Cost of Solar Collectors
The cost of solar collectors varies depending on the type, size, and brand. On average, flat plate collectors range from $300 to $1,500, while evacuated tube collectors can cost between $1,000 and $3,000. Concentrating collectors are typically the most expensive, with prices starting from $2,000 and going up depending on the scale of the system. While the initial cost can be high, the long-term savings in energy costs and reduced reliance on conventional energy sources make solar collectors a worthwhile investment.
Conclusion
Solar collectors are an essential component of solar thermal systems, providing an efficient and sustainable way to harness solar energy for heating purposes. Whether used for residential water heating, space heating, or industrial applications, solar collectors offer significant environmental and economic benefits. With various types available, including flat plate, evacuated tube, and concentrating collectors, there is a solar collector system suitable for every need and climate. Despite their initial cost, the long-term savings in energy bills and minimal maintenance requirements make solar collectors a smart investment for anyone looking to reduce their carbon footprint and save on energy costs.







